7.3. Lineage
What is Data and Model Lineage?
Data and Model Lineage in Machine Learning Operations (MLOps) refers to the comprehensive tracking of data and model origins, transformations, and dependencies throughout the machine learning lifecycle. It provides a historical record of how data flows through various stages, from its initial source to the final model outputs, which is crucial for understanding, debugging, and ensuring the reliability of AI/ML systems.
Lineage tracking encompasses:
- Data Origin: Identifying the initial source of data, including databases, APIs, or files.
- Data Transformations: Recording all processing steps applied to the data, such as cleaning, feature engineering, and aggregations.
- Model Training: Capturing details about the model training process, including hyperparameters, training data used, and resulting model versions.
- Model Deployment: Tracking where and how the model is deployed, including serving infrastructure and deployment timestamps.
Why do you need Data and Model Lineage?
Lineage information offers multiple benefits for managing and deploying machine learning models effectively:
- Debugging and Troubleshooting: When an issue arises, lineage information helps trace the origin of the problem by providing a clear picture of the data flow and model dependencies.
- Data and Model Governance: It enables auditing and compliance by providing a transparent record of data usage, transformations, and model versions.
- Reproducibility: It enhances reproducibility by documenting the exact steps involved in creating a model, making it easier to recreate results or validate findings.
- Impact Analysis: Lineage data can be used to assess the impact of changes to data or models on downstream applications or business processes.
What are the main Data Lineage use cases?
Data Lineage provides critical insights into the flow and usage of data within your ML projects, which can be invaluable for various purposes. Here are some common use cases:
Data Discovery
Lineage information makes it easier to discover and locate relevant datasets within your MLOps system. By tracing the lineage of models or predictions, you can identify the source datasets used, understand their characteristics, and explore their relationships with other datasets. This discovery process simplifies finding the right data for new projects or validating the suitability of existing datasets for specific tasks.
Impact Analysis
Understanding the impact of changes to data or models on downstream processes is crucial for maintaining system reliability. Lineage information facilitates this analysis by providing a visual representation of data dependencies. For example, if you make changes to a feature engineering step, you can use lineage tracking to determine which models rely on those features, allowing you to assess the potential impact on their performance and take necessary actions, such as retraining or retesting affected models.
Data Governance and Compliance
Meeting regulatory requirements and maintaining data quality often necessitate a clear understanding of data usage and its transformations. Lineage tracking offers a robust audit trail for data provenance, which can be used for compliance reporting and to ensure adherence to data governance policies. For example, tracking the lineage of personal data used in ML models can help demonstrate compliance with privacy regulations like GDPR, ensuring that data is processed and used according to established guidelines.
How to Implement Lineage Tracking with MLflow Datasets?
The MLOps Python Package leverages MLflow's Dataset API to log dataset information during the execution of various jobs, such as training or tuning. This provides a streamlined method for integrating lineage tracking directly into the MLflow tracking system, ensuring that dataset details are captured alongside model metrics and parameters.
Implementing Lineage Tracking in the MLOps Python Package
Here's how lineage is implemented within the MLOps Python Package:
-
Defining Dataset Readers: Within the
bikes.io.datasetsmodule, theReaderclass serves as an abstract base class for all dataset readers. It defines thelineage()method, which is responsible for generating lineage information.import abc class Reader(abc.ABC): @abc.abstractmethod def lineage( self, name: str, data: pd.DataFrame, targets: str | None = None, predictions: str | None = None, ) -> Lineage: -
Implementing Lineage in Concrete Readers: Concrete readers, such as the
ParquetReader, implement thelineage()method, utilizing themlflow.data.pandas_dataset.from_pandasfunction to create an MLflow Dataset object. This object captures the dataset's name, source, schema, and profile information.import mlflow.data.pandas_dataset as lineage import pandas as pd class ParquetReader(Reader): # ... (other methods) @T.override def lineage( self, name: str, data: pd.DataFrame, targets: str | None = None, predictions: str | None = None, ) -> Lineage: return lineage.from_pandas( df=data, name=name, source=self.path, targets=targets, predictions=predictions ) -
Logging Lineage in Jobs: Jobs, like the
TrainingJoborTuningJob, utilize thereader.lineage()method to generate lineage information for input datasets and then log this information to MLflow usingmlflow.log_input().# Within the TrainingJob's run() method inputs_lineage = self.inputs.lineage(data=inputs, name="inputs") mlflow.log_input(dataset=inputs_lineage, context=self.run_config.name)
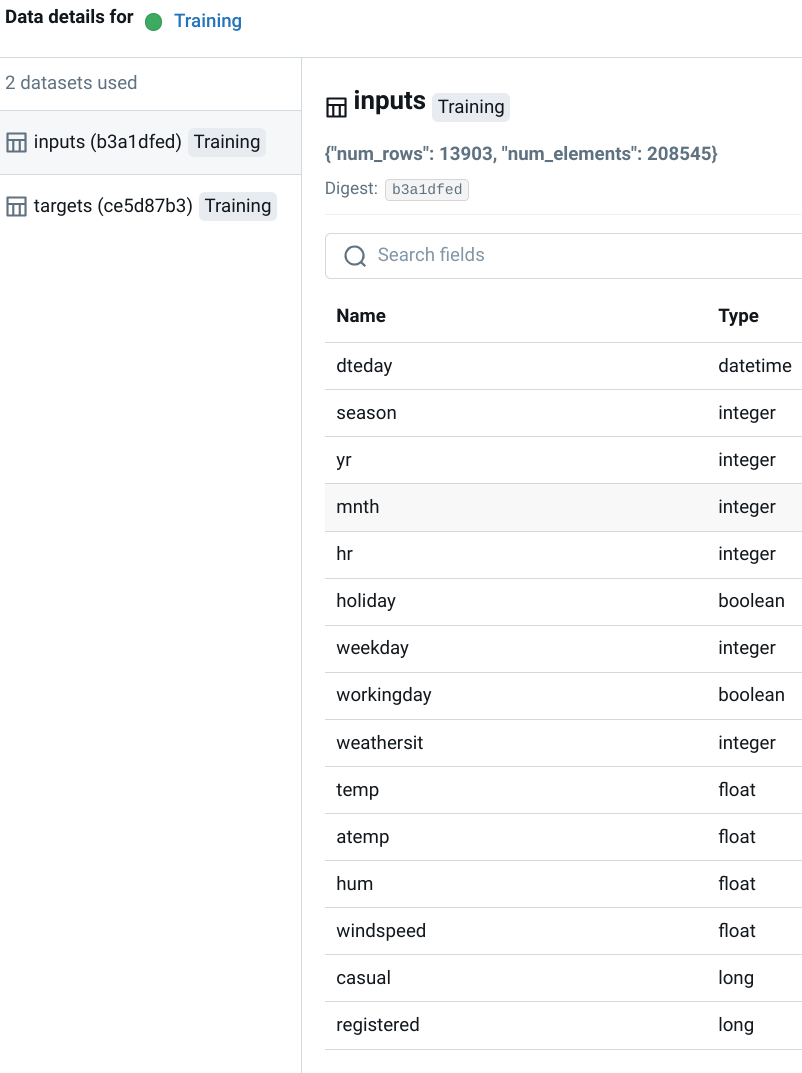
Visualizing Lineage in MLflow
The MLflow UI provides a visual representation of lineage information, enabling users to see the flow of data from its source to the models and predictions. This view simplifies understanding how different datasets are used within the project and facilitates debugging by tracing the lineage of specific models or predictions.
Enhancing Lineage Tracking
To further enrich lineage information, consider these practices:
- Log Transformations: During data preprocessing, include logging statements to record specific transformations applied. This can be done with custom tags or attributes within the lineage object.
- Utilize Data Versioning: Version control systems for data, like DVC, can be integrated to track different dataset versions used for model training or evaluation.
- Capture Feature Engineering Steps: Document the logic behind feature creation or selection to understand how features impact model outcomes.
- Track Model Deployment Lineage: Integrate deployment platforms with your lineage tracking system to capture where and how models are deployed.
By embracing these practices, you can significantly improve the transparency and auditability of your AI/ML systems.